Table of Contents (click to expand)
While a barcode only holds information in the horizontal direction, a QR code does hold information in both horizontal and vertical directions. Due to this, a QR code holds hundreds of times more information than a barcode.
A few days ago, I went to a grocery store with a friend. At the billing counter, the seller routinely flashed a handheld device at a specific point on the product’s packaging, and just as the device was “beeping,” he picked another product and repeated the same process.
“You see these black parallel lines? They form a barcode,” my friend informed me.
“Yes, I know, but do you know what they do?” I asked, to which he flashed the following expression:
We encounter barcodes almost every time we buy something in a store, but what do they actually do? And how do they differ from the increasingly popular QR codes?
Recommended Video for you:
What Is A Barcode?
Anyone who buys stuff from stores must have seen barcodes; however, whether or not they realize it’s a barcode they are looking at is a different matter altogether!
A barcode is a visual representation of machine-readable information about the product they are attached to.
To the layman, a barcode is a small box printed on the packaging of a product and has a small collection of black parallel lines of varying widths.

This is not just another box that is printed on the cover of the product, but also contains important information such as manufacturer name, article type, price, etc., which can only be read by special barcode readers. Since it consists only of data stored in a horizontal direction, it is also referred to as linear or 1D-1-dimensional.
What Is A QR Code?

Quick Response Code, often abbreviated as QR code, is similar to a barcode. In fact, it is a kind of barcode. Like barcode, it also contains machine-readable information about the object it is attached to. Unlike a normal barcode, however, a QR code is two-dimensional, i.e. it contains information in both the vertical and horizontal directions.
QR codes contain a lot of information. From large companies to the grocery store next door, everyone can create their own QR code and attach it to their products. For example, the QR code of the URL of our website reads:

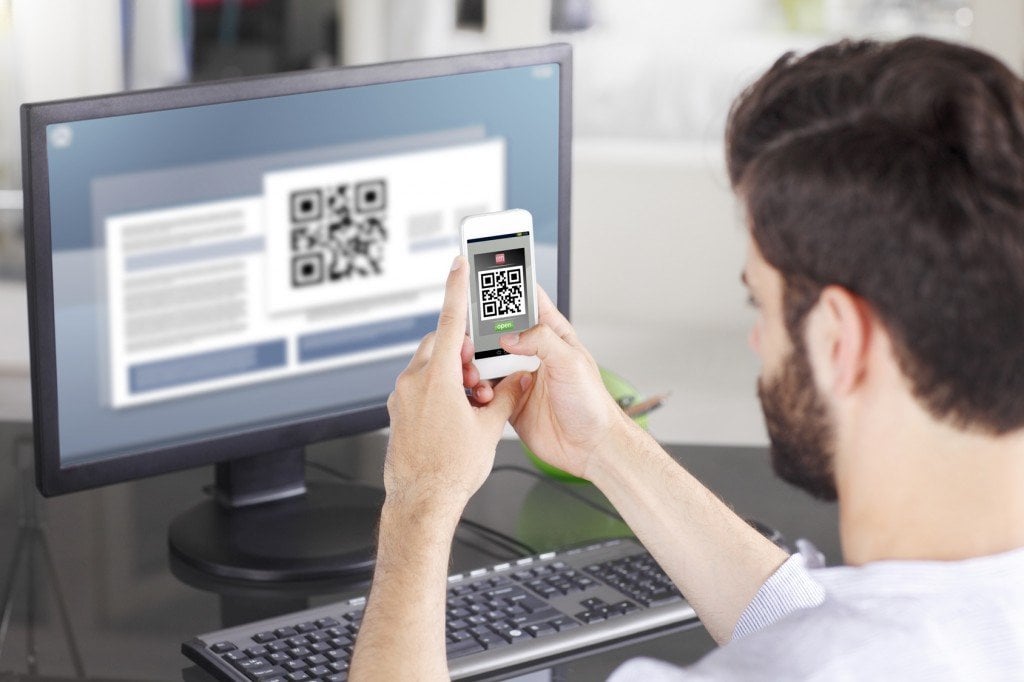
QR codes have grown in popularity over the last decade due to the rise of smartphones. There are certain QR code scanner apps that can be downloaded for free on smartphones. So once you see a QR code, just scan it with your phone’s app, the app usually uses the phone’s main camera to scan the code, and the pre-set action such as opening a web page, sending a tweet, downloading an app etc. that is attached to the code is triggered.
How Does A QR Code Differ From A Barcode?
Although both QR codes and barcodes serve the basic purpose of storing information about a particular product or organization, there are some major differences between them.
Appearance
One of the biggest differences comes in terms of the differences between their design or simply how they look. Take a look at the QR code and barcode of the URL of our website www.scienceabc.com.

The one can be easily distinguished from the other by a cursory glance.
Information Retention Capacity
This also applies to the design of the two codes. Whereas a barcode only contains information in a horizontal direction, a QR code contains information in both a horizontal and a vertical direction, hence the name “2-dimensional code.” Due to this structural difference, a QR code contains a hundred times more information than a barcode and has a greater potential to store more information in a smaller space than a barcode.
Adaptation And Error Correction
This is by far the most desirable advantage of QR codes over conventional barcodes. QR codes have an error rate of 7-30%.
Simply put, even if the packaging of the product in question or the printed code is damaged or soiled, the QR code works.
This feature is smartly used by companies and businesses. Because of the error-correction feature, they can (and do) put a small logo or a picture within the code to make it more associable to the business in question.
While bar codes have been around for more than a few decades, QR codes have only been a “trend” since the beginning of the last decade, thanks to the boom in smartphone absorption among consumers. And from now on, it seems that QR codes will remain until the popularity of augmented reality produces a completely different coding system.