Table of Contents (click to expand)
When water freezes, its molecules get arranged in a crystalline structure, thereby attaining a defined shape. This crystalline structure is less dense, and since there are gaps between individual molecules in the structure, the overall volume increases and water ‘expands’.
From a cursory glance, the phrase “water expands when it freezes” may not make sense, because in liquid form water has no definite shape or form, and therefore seems to occupy more space. Also, when it freezes, water takes on a clearly defined form, which seems quite the opposite of “expansion.”
Let me therefore begin by breaking down the question posed in the title of the article.

Recommended Video for you:
Does Water Really Expand When It Freezes?
Yes, water expands when it freezes. Note that the word “expands” in this sentence indicates an increase in volume. So, a technically sound way to put it would be—water’s volume increases when it freezes.
This statement is accurate, and you can test its legitimacy with a simple experiment: if you lower the temperature of water, you will notice that the volume of the water decreases as it becomes more and more “intact.”
You can refer to the following chart to see how much does water expand when it freezes:
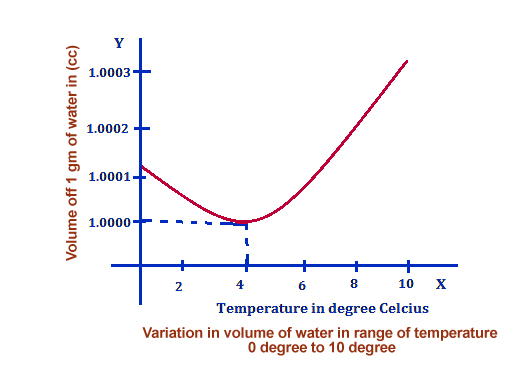
Now, let’s talk about why the volume of water increases or why it expands when it freezes and reaches a solid form.
Why Does The Volume Of Water Increase When It Freezes?
This phenomenon has to do with the chemical constitution of water. You see, a molecule of water is made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The arrangement of these atoms is quite unique, which gives water some special properties, such as the high heat capacity of the water, surface tension, adhesion, and cohesion.
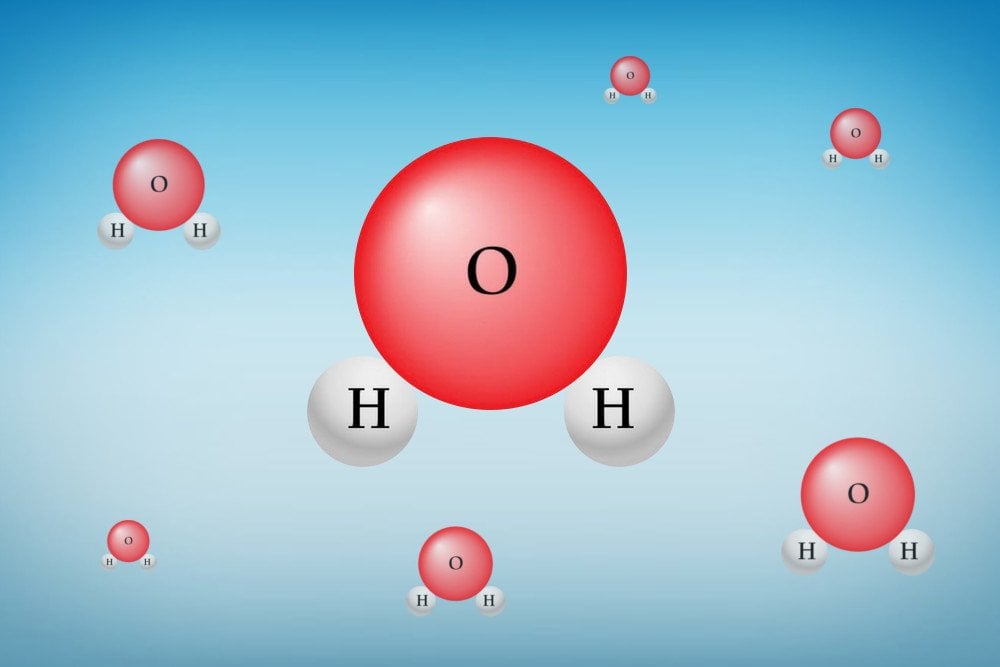
This arrangement of a water molecule creates a positively charged side near the hydrogen atoms and a negatively charged side near the oxygen atom.
When two water molecules come close together, the positive side of one molecule clings to the negative side of the other molecule. When this happens on a large scale (i.e. with millions of water molecules), what you get is a unique structure, which accounts for some of the chemical properties of water.
In liquid form, water molecules can move freely, forming and breaking hydrogen bonds in the process, a property that accounts for the irregular shape of water (or any liquid, for that matter). Some water molecules are often “stacked” on top of each other, which explains the higher density of water, as compared to ice.
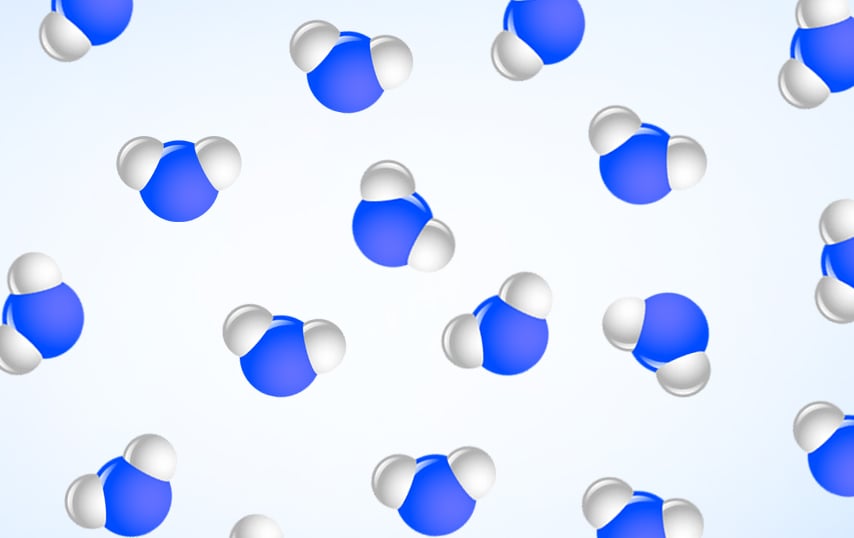

However, as the temperature drops and the water cools down, the intermolecular forces increase, the freedom of movement of water molecules decreases, and they become less and less energetic (with decreasing temperature).
When water reaches its freezing point, the movement of its molecules becomes negligible as they take on a more defined shape, arranged in six-sided lattices.
Below is an oversimplified version of the arrangement of water molecules in their crystalline form in ice:
This crystalline arrangement of water molecules is less dense, as it prevents molecules from huddling up (as happens in the liquid form) due to stronger intermolecular forces.
This spacing of molecules and keeping them fixed in that position increases the volume of water, which is why it’s said that water expands when it freezes.
This Is Why Ice Floats On Water
Water expands when it becomes ice, and since the volume is inversely proportional to the density of a substance, ice is less dense than water. For this reason, ice, a substance that appears heavier than its liquid form, floats on water.
If water didn’t expand when it froze, then ice would be denser than water. Think of the impact on the ecosystem of the planet! Ice on the surface of lakes, seas and oceans would sink and these bodies of water would gradually fill from bottom to top. With frozen lakes and oceans, there would be no aquatic life on Earth.
From that perspective, it’s a very good thing that water expands in its solid form!













