When you use Bluetooth headphones, you are making direct contact with the device. In a way, yes, you are better off not using a Bluetooth headset if minimizing exposure to electromagnetic radiation is your primary concern.
Since the turn of the millennium, interconnection between electronic devices has become increasingly wireless. This wireless interconnection primarily comes in the form of electromagnetic radiation, which in recent times has been subjected to many health concerns.
Recommended Video for you:
Wireless Technology And Radiation Conundrum
In this age of the internet, smartphones are nearly indispensable, and they primarily run on cellular networks. Besides cellular networks, we also use two other wireless technologies: Bluetooth and Wifi.

I recently saw one of my cousins who is expecting a baby. She was very jittery about electromagnetic radiation, especially for the child about to come into her life. She asked me if it would be better if she avoided using Wifi and Bluetooth. She wondered whether turning Wifi and Bluetooth off would exposed her to significantly less radiation.
Well, while the idea of cutting out Wifi and Bluetooth seems to be prudent, when you get into the technicalities and science of wireless communication, the answer isn’t that straightforward.
Wifi and Bluetooth both use radio frequency signals, which are part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The mobile network that you use by inserting a SIM card into your cellphone also works on radio frequencies. Now, how much you are exposed to electromagnetic radiation depends on a couple of factors, including the strength of the signal, the distance of the emitting device from your body, the mode of communication used, etc.
Wifi: Non-ionizing Form Of Radiation
Another important thing to consider is that the radio frequency signals that Wifi and Bluetooth work on are non-ionizing forms of radiation. What this simply means is that these radio waves don’t have enough energy to affect or alter your DNA—the building blocks of life. Altering one’s DNA is bad, as it can open the door for life-threatening diseases.
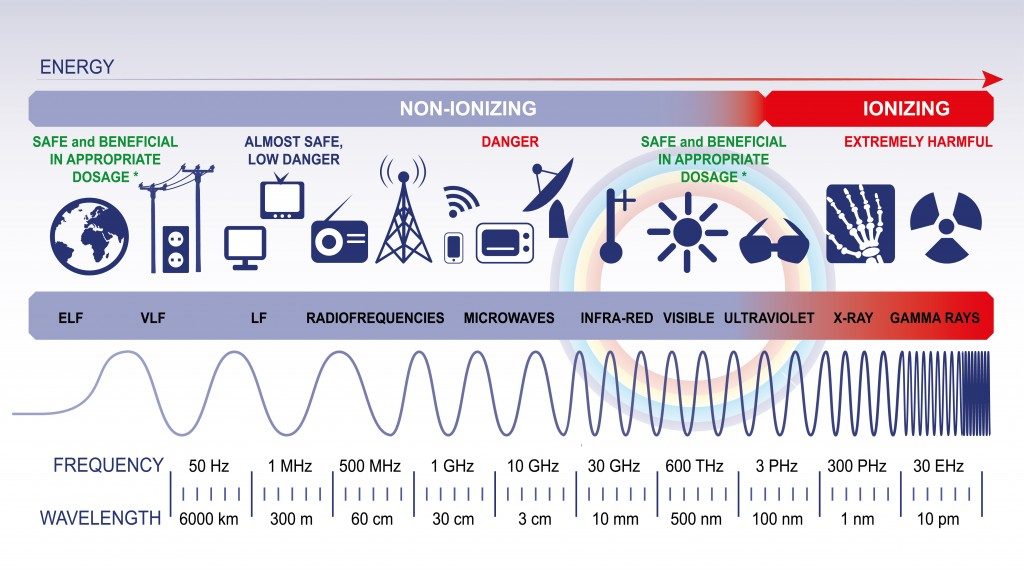
Now, a few studies have hinted that even non-ionizing radiation can have measurable effects on cells and tissues, but how serious they are is still subject to much debate.
One such study conducted by the National Institutes of Health under the National Toxicology Program found a potential carcinogenic effect of radio waves on rats. Several rats and mice were studied, and exposed to radio frequency radiation for a few hours. Six percent of the male rats exposed to the radiation were found to develop cancer. Interestingly, none of the female rats developed cancer.
So, while the research wasn’t really conclusive, it hinted at a strong correlation between cancer and exposure to radio waves.
It’s All Radio Waves!
The point is that all three wireless communication methods—cellular network, Wifi, and Bluetooth—use radio waves. However, we generally keep our mobile phones ON most of the time, so our mobiles are incessantly transmitting radio waves (unless you put it on an airplane mode). This cellular network coverage is the major source of radiation. That being said, this does not mean that Wifi and Bluetooth don’t add more, but their contribution is less, given that their signal strength is weaker than cellular signals. Thus, their potential impact is also less. Now, this ‘weakness’ of signal is still debatable, considering that it’s not absolute and depends on a number of factors, including the strength of the signal and distance from the body.
Inverse-square Law At Play
These radio waves obey the inverse square law when it comes to distance. What this means is that by increasing the distance between your body and the device, you can exponentially reduce your exposure. For example, if you double the distance, the exposure would be reduced by four times.
If you think about it in such terms, the most exposure you can get is when you talk over the phone. While on the phone, you are bringing your phone really close to your skull, and thus your brain. The surface area in touch with your body is at a maximum, so talking over the phone poses a greater radiation risk (Source) than simply keeping the phone in your pocket.
Similarly, when you use Bluetooth headphones and turn them on to listen to music, you are again making direct contact with the device.
Thus, you are better off not using a Bluetooth headset if minimizing exposure to electromagnetic radiation is your primary concern.
Similarly, doing video calls instead of phone calls with wired earphones is a good option.

The concern related to Bluetooth has now been addressed, but what about using Wifi? Well, it’s better to use Wifi than cellular data, because the power that WiFi signals carry is much lower. Cellular signals that your cellphone works on are emitted by cell towers, which exude radio waves at around 50 watts. Wifi routers, on the other hand, typically work on 4 watts or less.
Even so, remember that the absorption of these waves depends very much on the distance, i.e., the closer you are to a cell tower or a router, the higher the radiation density.
SAR: A Good Benchmark To Assess Radiation Intensity
The specific absorption rate is a good parameter to assess how much radiation our bodies absorb upon exposure to these wireless devices. The SAR value for a typical Wifi signal operating at least half a meter away from the router is less than 0.01 W/kg. Compare that to the SAR value of flagship smartphones, like the iPhone 12 Pro of 0.99 W/kg.
As you can see, the answer to whether turning off Wifi and Bluetooth would substantially help you in reducing radiation exposure isn’t that simple.
For example, if you turn off these two and continue to use the cellular network for calls and the internet, you are still exposed to substantial amounts of radiation. Also, since Bluetooth devices like headphones or smart bands are wearable gizmos, you are risking yourself more through this direct contact (Source).
Finally, when it comes to choosing between cellular data and Wifi, it’s definitely better to choose Wifi, as the intensity of Wifi signals in terms of SAR value is far less. Moreover, you’ll substantially save on your battery, which is always a good thing!
References (click to expand)
- YH Ahn. Hsd:Sprague Dawley SD Rats Exposed to Whole-Body Radio .... The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences
- Delhi, N., & Behari, J. (n.d.). Electromagnetic pollution-the causes and concerns. Proceedings of the International Conference on Electromagnetic Interference and Compatibility (IEEE Cat. No.02TH8620). IEEE.
- Cellphones, wi-fi and electromagnetic radiation | NBR - www.nbr.co.nz