Table of Contents (click to expand)
LED (or Light Emitting Diode) lights have become quite a worldwide sensation due to their energy efficiency and long-lasting characteristics. LED lights are capable of converting 30-40% of the consumed energy into light.
Don’t be an old-fashioned tube light! Be a trendy LED bulb instead.
Light Emitting Diode or LED is a type of PN junction diode. It is made up of semiconductor material that generates light when current flows through it. It works on the principle of electroluminescence and is used for our day-to-day lighting purposes.

You have likely noticed the rising popularity of LED lights and bulbs in the past decade or so. Most of our lighting needs are fulfilled by LEDs today, replacing incandescent bulbs and even CFLs (Compact Fluorescent Lamps). LEDs have been labeled as highly energy-efficient and long-lasting, but what is the reason behind their superiority?
Let’s explore more about the science behind these LED lights and make our lives a bit brighter.
Recommended Video for you:
How Do LED Lights Work?
LED lights are made of small light-emitting diodes that are shaped according to individual requirements. To understand how an LED light works, we have to get into the details of how an LED works in the first place.
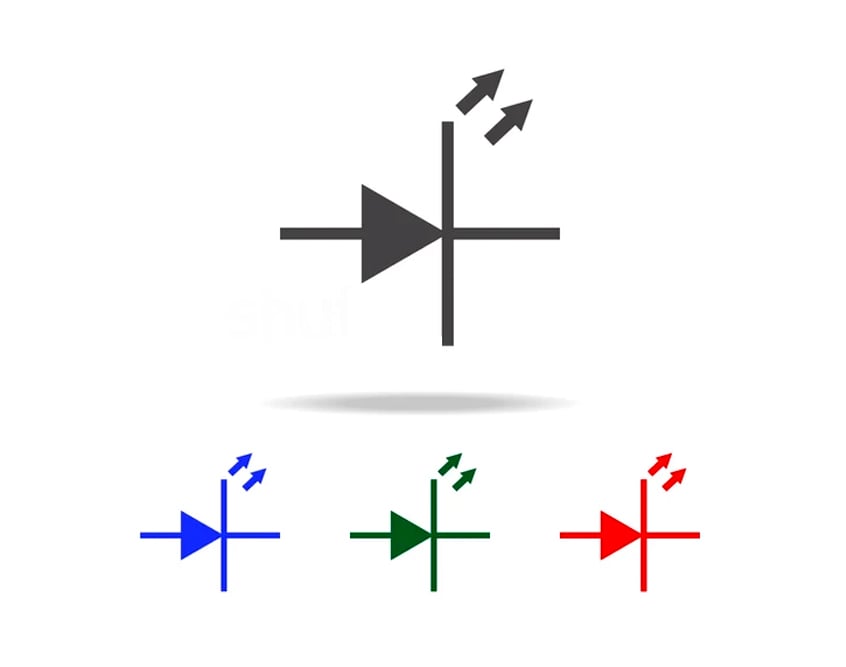
An LED is made up of semiconductor material in the form of a PN junction diode. It emits light in the forward bias (higher voltage is applied to the P-end of the diode than the N-end of the diode) and current flows from P to N. In forward bias, when the holes from the p-type region enter the junction and recombine with the electrons from the n-type region of the LED, energy is released mainly in the form of photons (packets of light). These photons emit light.
Different doping chemicals are added to the LED to emit different colors of light. For example, Aluminum is added to the Gallium Arsenide diode for the emission of visible red light.
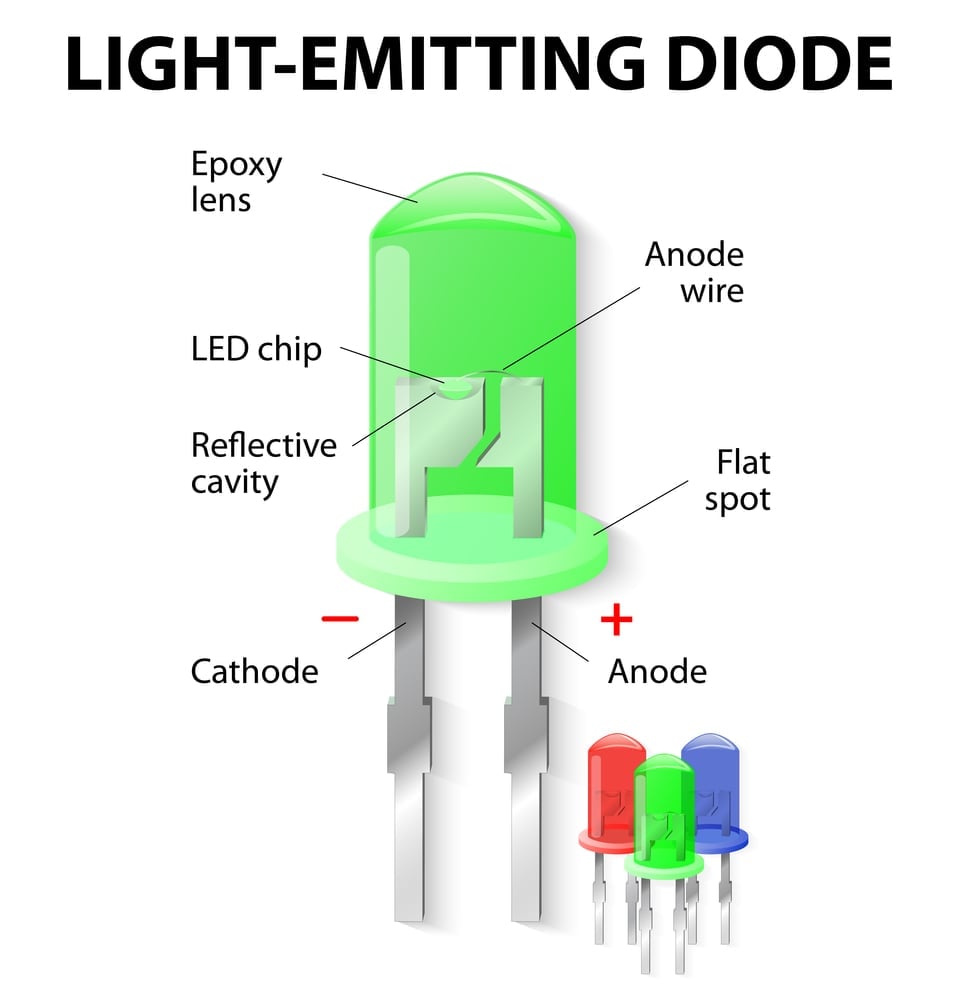
Therefore, an LED light works on the principle of electroluminescence to produce light. A point to note here is that an LED runs on Direct Current (DC), but the power supply in domestic households is in the form of Alternating Current (AC). Therefore, there is a built-in voltage driver at the base of LED lights that converts the 120-240 V AC current to 30-60V DC current for proper function.
How Are LED Lights Different?
The world has changed and technology has evolved. Thirst for a better way of living has led to exceptional inventions and discoveries, LEDs being one of them.

LED lighting is quite different from other types of lighting, like incandescent and CFL, due to the many advantages that it has over them.
1) Wide Range Of Colors
LEDs are extremely small and can emit a wide range of colors. It’s easy to produce different colors from LEDs, so they are extensively used in decorations and electronics.
2) Directional Lighting
LEDs emit light in only one direction, which reduces the need for reflectors and diffusers that may result in a loss of light. This feature makes LEDs an ideal choice for recessed down lights and task lighting.
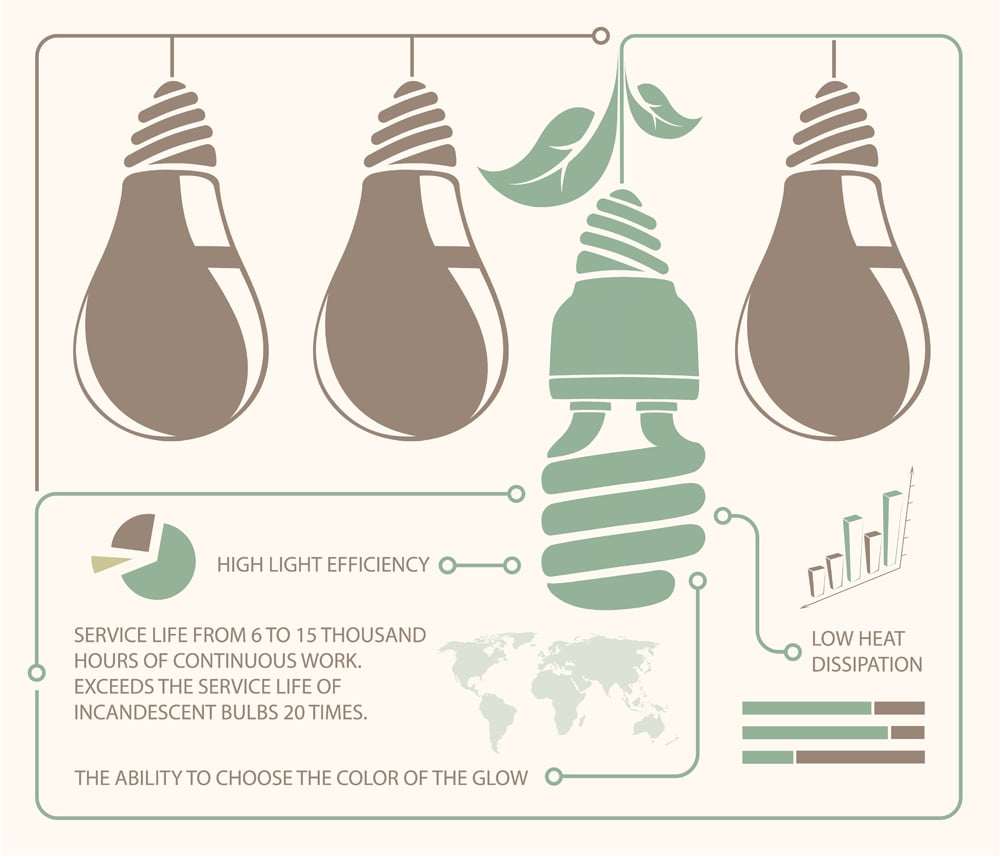
3) Minimal Heat Dissipation
LEDs emit negligible heat energy, as the vast majority of energy is released in the form of light. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which emit 90% of their energy as heat, and CFLs, which emit 80% of their energy as heat.
4) Long Life
LED bulbs last significantly longer than other bulbs because they don’t have any parts that burn down like a filament or break down over time. LEDs can last up to 25,000 hours—almost three years of constant use.
Why Are LED Lights So Energy-efficient?
LED lights use up to 75% less energy than conventional forms of lights.
LEDs are themselves the source of photons. They generate photons (light particles) when the current is passed through them. They have no filaments or materials that need to be burned to produce light. About 30-40% of the consumed energy is emitted as light, while the rest is lost as heat. LEDs are wildly energy efficient because the wastage of energy is kept to a minimum.
In incandescent bulbs, the filament material must be heated by the flow of current until it glows, which then emits light. In this process, about 90% of the consumed energy is lost due to thermal radiation and only 10% is emitted as light.
In CFLs, on the other hand, the current is passed through a tube containing argon and mercury vapor and this action generates light energy. However, again, only 20% of the consumed energy generates light, due to a significant loss in the form of heat energy.
LED lights deliver more lumens (quantities of visible light) per watt than incandescents. They have higher luminous efficacy. 60-watt incandescent bulbs can roughly generate up to 900 lumens, whereas an LED bulb uses only 6-8 watts for the same luminosity.
LED Lights Are Worth It!
LED lights are capable of changing the lighting scenario of the globe completely in the near future. They are also widely used in electronics and gadgets like LED Televisions, watches and mobile screens.

Long-lasting, money-saving, and extremely efficient, LED lights are power-packed. They are worth a try and will undoubtedly light up your world!