Table of Contents (click to expand)
High heat can significantly damage your electronics, potentially causing issues like resistance, melting, short circuiting, and battery deterioration. It’s crucial to be aware of these risks and take preventive measures to protect your devices from heat-related damage.
Have you ever experienced the scorching sun turning your smartphone into a mini oven or wondered why your computer’s fan seems to work overtime during demanding tasks? Believe it or not, high heat can play tricks on your electronic gadgets, causing them to misbehave in serious ways. In this article, we’re going to uncover the mysteries of how and why high temperatures can wreak havoc on your beloved electronics.

Recommended Video for you:
The Basics Of Electronics And Heat
Before we delve into the world of heat and electronics, let’s take a quick journey to understand how our gadgets operate. Electronics, like smartphones and computers, are intricate puzzles made of tiny pieces—microchips, transistors and circuits. These components collaborate to process information and perform the tasks we assign them.
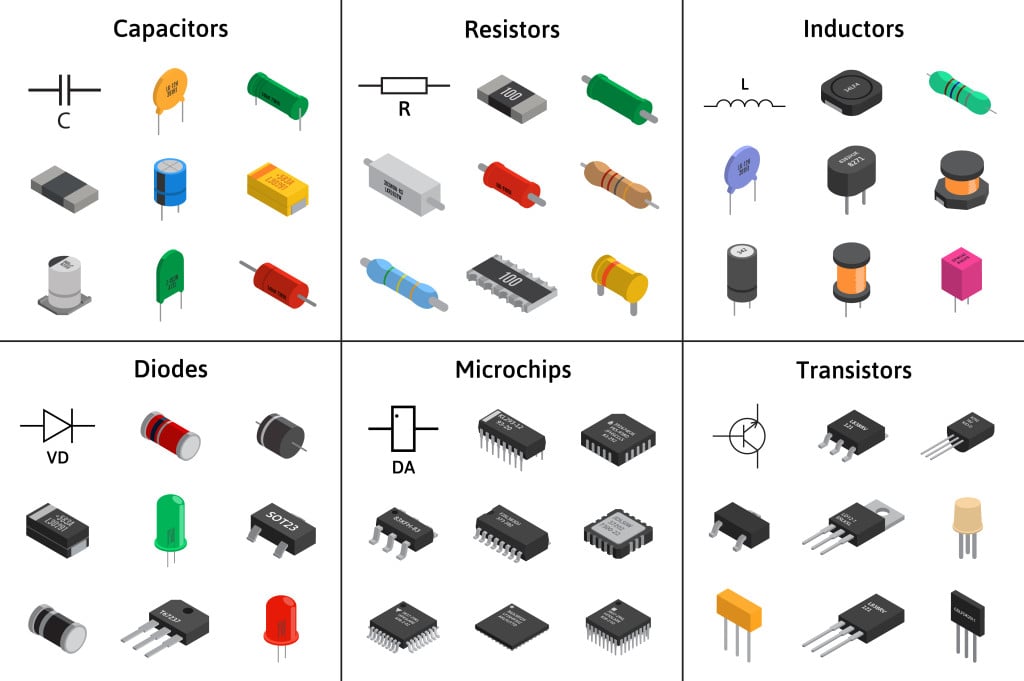
Now, here’s the twist: electronic devices have their own comfort zones when it comes to temperature. If things get too hot, trouble starts brewing.
Heat And Resistance
Imagine trying to weave your way through a bustling crowd. The more people you have to push through, the tougher it becomes, right? Well, in the world of electronics, resistance works in a similar way. Resistance is the opposition that an electrical current faces while traveling through materials inside your gadgets.
When electronics heat up, the materials they’re made of can become more resistant. This is a big headache because it hinders the smooth flow of electricity. Consequently, electronic components must toil harder to carry out their duties, and this extra effort generates even more heat, leading to a never-ending cycle of trouble.

The Melting Point Dilemma
Every material, from metals to plastics, has a breaking point—a temperature at which it transforms from a solid to a gooey mess. When the temperature inside an electronic device surpasses this melting point for certain components, it’s like opening Pandora’s box. Parts can warp, solder joints (used to connect components) can snap, and connections become about as reliable as a leaky faucet.
Take solder, for instance, which is the “glue” holding your gadgets together. When things get too hot, it can melt, causing components to lose their grip or disconnect entirely.
However, it’s important to note that the temperatures required to melt solder are significantly higher than what a device is likely to reach under normal operating conditions. These issues typically arise only under extreme conditions, such as in high-heat environments or during prolonged exposure to intense heat.
Short Circuits And Electrical Fires
Heat doesn’t just stop at causing resistance and melting components. It can also lead to short circuits and even fiery disasters. A short circuit happens when electricity takes an unintended detour due to damaged components or exposed wires. High temperatures make this problem worse by weakening insulation and causing wires to expand or contract, creating potential electrical mishaps.
It’s crucial to emphasize that most electrical connectors and components are designed to accommodate regular ambient temperatures without causing breakdowns. These issues typically arise in extreme conditions where temperatures are far higher than what a device would encounter under normal circumstances.
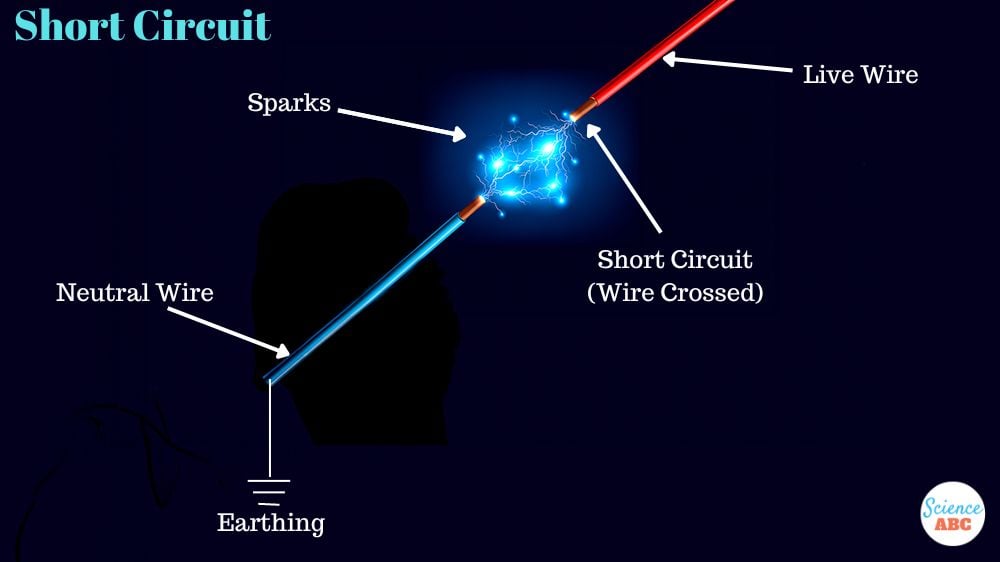
In extreme cases, excessive heat can trigger fires within electronic devices by igniting flammable materials. That not only spells doom for your device, but can also put your safety in jeopardy.
Silicon And Semiconductors
Many of our gadgets, from smartphones to laptops, rely on the remarkable world of silicon-based microchips and transistors. These minuscule marvels serve as the brains behind your devices, working tirelessly to perform intricate calculations, process data, and execute the tasks we assign them.
It’s worth noting that silicon components are sensitive to heat, but everyday use rarely exposes them to extreme temperatures. For high-performance silicon devices, the optimal operating temperature is generally below 150°C.
Beyond this, they can lose efficiency due to increased power loss caused by higher leakage current in the off-mode. Think of these devices as precision instruments. When they get too hot, their performance may decrease, resulting in sluggish performance, delayed responses, and, in the worst cases, complete malfunction.
The Impact Of Heat On Batteries?
Lithium-ion batteries, the powerhouses within cellphones and electric vehicles, have a love-hate relationship with heat. When faced with scorching climates above 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), these batteries tend to throw in the towel.
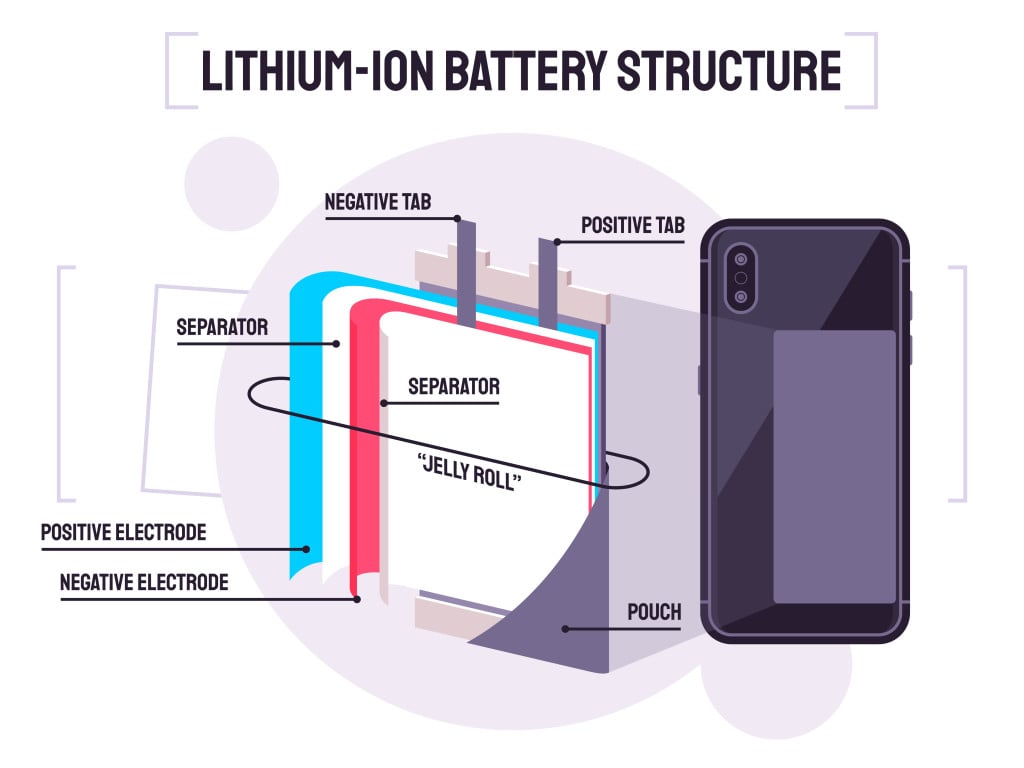
Higher temperatures make the chemical reactions inside the battery go haywire, causing corrosion that drains the lithium and shrinks the battery’s storage capacity. Electric vehicles can lose some of their driving range when exposed to a relentless 90-degree Fahrenheit heatwave.
Excessive heat can accelerate the battery’s self-discharge rate, causing it to lose charge faster when not in use. Furthermore, it can lead to irreversible capacity loss, meaning that your battery won’t be able to hold as much charge as it did when it was new. This ultimately results in a shorter overall battery life.
To protect your battery in hot weather, avoid leaving your devices in the sun, reduce power-intensive activities, monitor battery temperature, and use battery-saving modes when necessary.
Effects On Display Screens
Your device’s display screen acts as a window to the digital world, but extreme heat can cause issues related to screen visibility. When exposed to high temperatures, the screen may develop condensation or fogging, similar to a window misting up in hot and humid conditions. This fogging effect can reduce the clarity of the screen, making it harder to see the content.
Prolonged exposure to scorching heat may result in permanent damage to the screen, causing issues like discoloration, dead pixels, or touch insensitivity.
To safeguard your screen, avoid leaving your devices in hot cars, where temperatures can easily skyrocket. Seek shade when using your gadgets outdoors, and consider using a cover to shield them from direct sunlight. You can also adjust the screen brightness to reduce heat generation.
Cooling Solutions
Fortunately, manufacturers aren’t oblivious to these heat-related dilemmas. They’ve armed your gadgets with cooling mechanisms like fans, heat sinks, and thermal paste to whisk heat away from critical components.
Have you ever wondered why your computer’s fan goes into overdrive during intense tasks? It’s a sign that the device is pulling out all the stops to stay cool without compromising performance. The fan expels hot air from inside the computer, saving it from an overheating crisis.

Protecting Your Electronics
Now that we’ve unraveled the mysteries of heat and electronics, how can you shield your gadgets from this fiery foe? Here are some nifty tips:
- Shade and Shield: Just like you might seek shelter under a tree on a scorching day, shield your devices from direct sunlight. Hot weather and bright sunshine can be a recipe for disaster.
- Breathe Easy: Your gadgets need to breathe. Ensure that they have proper ventilation and don’t block cooling fans or vents.
- Dust Patrol: Regularly clean your gadgets to prevent dust buildup, which can lead to overheating.
- Temperature Care: Keep your electronic devices in places with a stable and moderate temperature. Avoid extreme heat whenever possible.
- The Heat Wave Shutdown: If the temperature is off the charts, consider giving your gadgets a break by shutting them down. It’s a protective measure that could save you from future headaches.
In a world where electronics have become an integral part of our daily lives, understanding the intricate dance between high heat and your gadgets is paramount. From resistance and melting points to short circuits and electrical fires, it’s clear that heat can wreak havoc on your cherished devices. However, armed with knowledge and a few simple precautions, you can ensure that your electronics continue to serve you faithfully, even on a blisteringly hot day.
As you venture out into the scorching sun, be a tech-savvy hero and keep your devices cool and protected! By following these guidelines, you’ll not only extend the life of your electronics, but also ensure your safety in the digital age. Stay cool, stay connected, and let your devices thrive in any weather!












