Table of Contents (click to expand)
Social media filters from Snapchat and Instagram that change a user’s facial features work using a technology called Augmented Reality.
I turned myself into a dog, a vampire, and a beauty queen with a full face of makeup today. In the space of mere seconds, I was able to transform completely, without ever lifting my head off the bed. That’s the kind of magic that Snapchat, Instagram, and other newfangled apps bring to us these days.
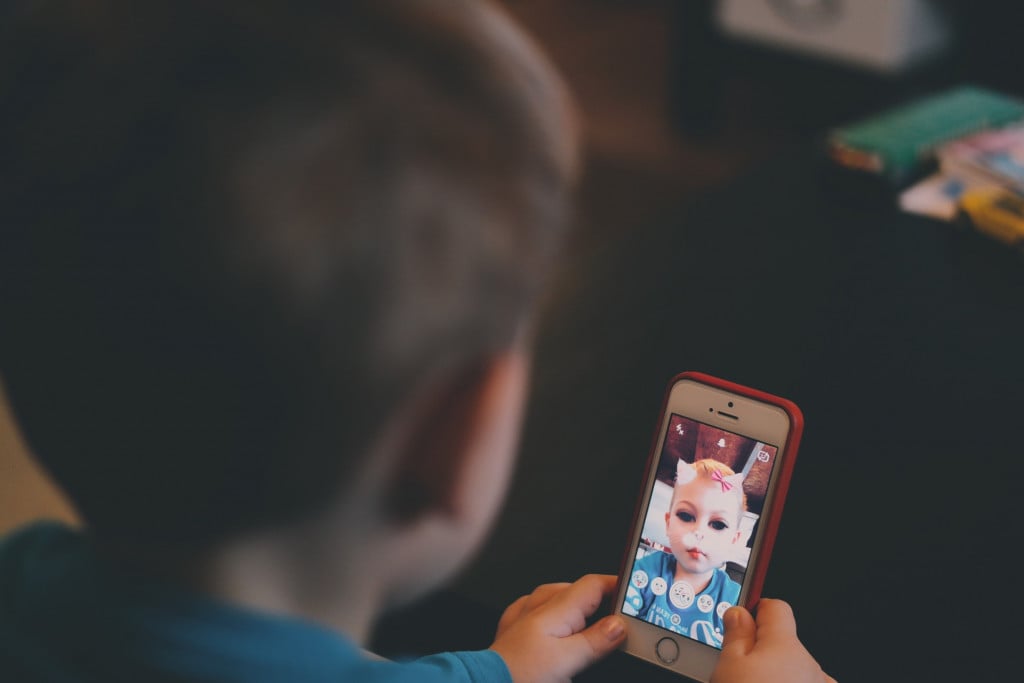

Filters that alter our facial features in real-time are nothing new, but they keep getting better and more realistic. However, what goes on behind the scenes of these filters? What trick of technology is actually running the show?
Recommended Video for you:
Where Did Social Media Filter Come From?
Facial recognition and modification is not a new invention. Facebook was finding and tagging faces in images a long time ago. It is the scale and the processing speed—the ability to do this in real-time—that is new.
The social media filter craze began back in 2015 when Snapchat acquired Ukrainian startup Looksery. At the time, they were the only player in the market with the capability to enhance live videos and images.
Now, everyone has this ability in their bag of digital tricks. Filters can now modify your facial features with almost eerie accuracy, and can even detect the world around you—making dancing cats appear on the pavement in front of you with little more than a tap.

A technology called Augmented Reality (AR) is responsible for all these new features. Snapchat, Instagram and Facebook have their own version of these filters, but they’re almost all the same thing. Some describe it all as ‘Social AR’, but more correctly, it’s a combination of computer vision, AR, and Artificial Intelligence (AI).
Augmented Reality (AR): Technology That Powers Filters
Augmented Reality is a technology that allows real-world images to be enhanced and modified. You can combine the virtual world with the real world, overlaying one on the other.

AR is an advanced technology that has capabilities extending far beyond dog filters, but for the time being, we’re talking about these basic filters. In its basic form, AR overlays images on the live video being captured by a camera. For your social media needs, your smartphone camera usually serves this purpose.
How Do These Filters Work?
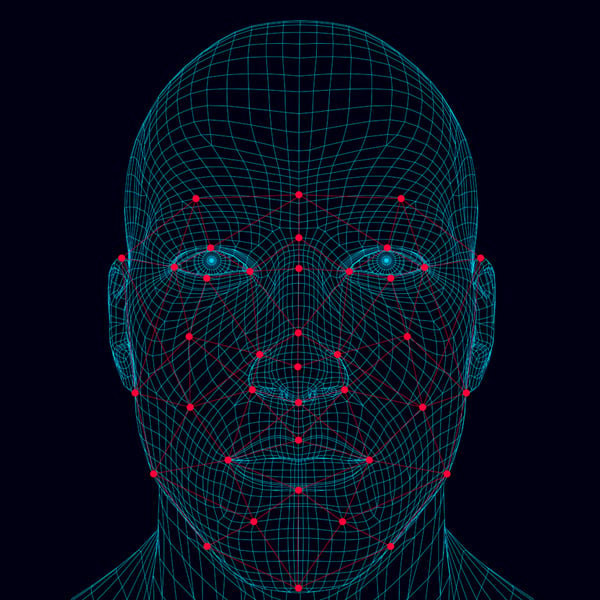
First, the computer needs to figure out where your face is. Then it maps out the features of your specific face, distorting and applying effects to your appearance.
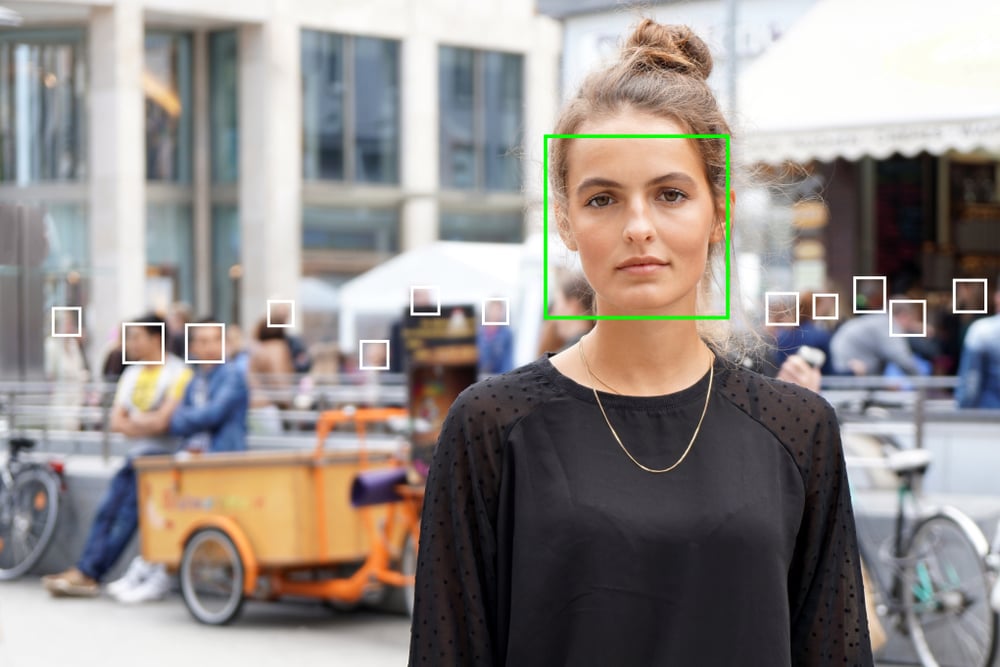
- Detection: Teaching computers to detect and recognize faces and facial features is no simple feat.

- The computer converts the image to greyscale to make it simpler to understand. It then analyzes the color values of the pixels in a picture and recognizes patterns of contrast. Something called the Viola-Jones object detection framework is used for this.
- Mapping: Active Shape Models (ASM) are used to find specific people and tag facial features. Machine learning models are trained using data where those features have already been mapped. A face has a set of points marked to define its features, forming a Point Distribution Model (PDM).
- Basically, you feed the computer a hundred images and tell them where the eyes are in every picture. The computer then becomes capable of pinpointing eyes in a fresh image.
- When you capture your own face using your camera, the computer places the points of an average face around where it detected your face to be. These points are adjusted according to their knowledge of how a face is “supposed” to appear. It then creates a ‘mesh’ of your face from these points.

- Modification: The 3D mesh of your face can move with you. That’s why the lipstick filter you apply doesn’t get shaken off when you move your face to one side. This mesh can be distorted to create desired alterations, i.e., it can make your face look puffy, your nose look pointy, or your eyes look bigger.
- Images are overlaid to create specific effects, like makeup. The image of the lipstick has points that are meant to match the points that indicate the position of your lips, which generates a very accurate positioning of the image.
And thus, voila! You’re puking rainbows!

Conclusion
Now perhaps you better understand how social media AR filters work. They use what they already know about faces to detect and map your face. Then they can do what they want with it, including make it into weird and silly shapes.
As the technology gets better in the future, AR filters will be so good at emulating reality that it will be impossible to tell what’s real and what’s not. For now, however, let’s just have some fun with bunny ears and colored hair.
References (click to expand)
- How do Snapchat filters work? Simple explanation - Technobyte. technobyte.org
- What Is Augmented Reality? | The Franklin Institute. The Franklin Institute
- AR Face Filters: How Do They Work and How Are ... - Knight Lab. Northwestern University
- Lu, H., & Yang, F. (2014). Active Shape Model and Its Application to Face Alignment. Studies in Computational Intelligence. Springer Berlin Heidelberg.