Table of Contents (click to expand)
“Dragon man” is the name of the skull of another species of human found in the Harbin area of the Heilongjiang province in China. On analysis, some scientists think the skull is of a new human species, Homo longi. However, other experts think the skull is similar to that of Denisovans, another species of human for which we have yet to discover a skull.
The story of Dragon man might be one of the most astonishing treasure hunt stories you’ve ever heard. This story has everything – smuggling, scientific debates, and the capacity to rewrite history as we know it.
And it starts like this…
In the year 1933, a construction worker stumbled upon what he thought was an old human skull. He found this mystery skull by the Songhua River, which runs through the Harbin area of the Heilongjiang province in China. The province’s name literally translates to Black Dragon River.
Therefore, in honor of the original location, the skull was nicknamed ‘Dragon Man’.

Now begins the odd series of events surrounding the discovery. This skull was allegedly smuggled into the construction worker’s home, where it remained hidden for 80 years!
On his deathbed, the worker revealed his discovery to his family. An anonymous family member then sought out a paleontologist. They donated the fossil to the Geoscience Museum, Hebei GEO University in China, where you might still find it today.
There was certainly speculation on the motives of the family member who brought the skull to light. Perhaps they were worried about the illegal possession of the skull, or simply didn’t like the idea of sharing their home with the dead. Whatever the reason, the paleontologist arranged for a discrete meeting and started working to uncover the truth of Dragon Man.
Before we move on, it must be noted that the paleontologist himself, Ji Qiang, doesn’t necessarily believe the entire story the family member told him, as it seemed too good to be true.
Recommended Video for you:
The Skull Of A New Species Of Humans
Scientists investigating this skull classified it as a new species and named this species—Homo longi. In order to understand the scientists’ interpretation, let us take a look at the sketch of the infamous skull ourselves.
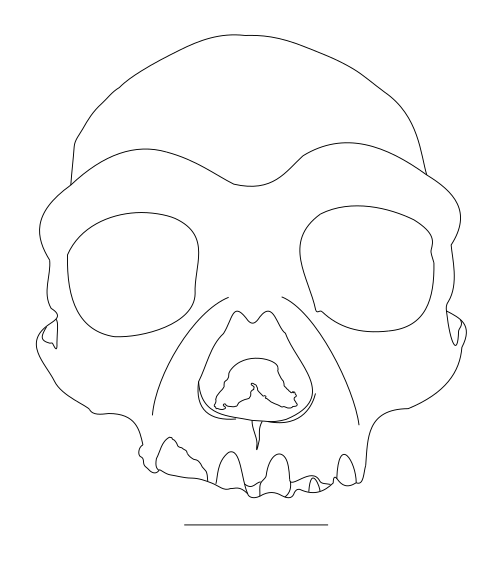

I would also urge you to look into the original article for some fantastic pictures of ‘Dragon Man’.
The paleontologist and his colleagues took a variety of measurements of the skull, including the cranial capacity (the part that houses your brain) and found that the cranium was larger than many other hominid species with a capacity of 1420 mL. This skull is surprisingly similar to modern man.
While describing the morphology of the skull, one of the authors said to Live Science, “[…] His face, nose and jaws were very broad, and he had big eyes. But his face was low in height, with delicate cheekbones, and it was tucked back under the braincase, as in a modern human.”
In addition to modern human-like features, this skull also had a strong brow ridge like the ancient, prehistoric man.
While investigating the unbelievable story of its discovery, the group confirmed that the skull was indeed from the Harbin area. They performed geochemical tests and concluded that the Dragon Man’s chemical composition resembles other fossils from that same locality. They claim that the skull is at least 146,000 years old, and perhaps even older.
This would put the age of its existence in the Pleistocene era—the era of the Great Ice Age!

Is It Really A New Human Species?
An important aspect that must be emphasized from the description of the skull is that the Dragon Man has a mix of modern (e.g., delicate cheekbones) and ancient (e.g., strong brow ridge) human-like features. This uniqueness is why scientists claim this species to be a new human species and call it our long-lost relative.
In order to understand where these species fit in our human evolutionary tale, scientists performed extensive computer analysis while comparing it with other known species.
Since we do not have DNA samples of all the skeletons discovered in the ancient era, scientists relied on the characteristics of the skull to generate a family tree.
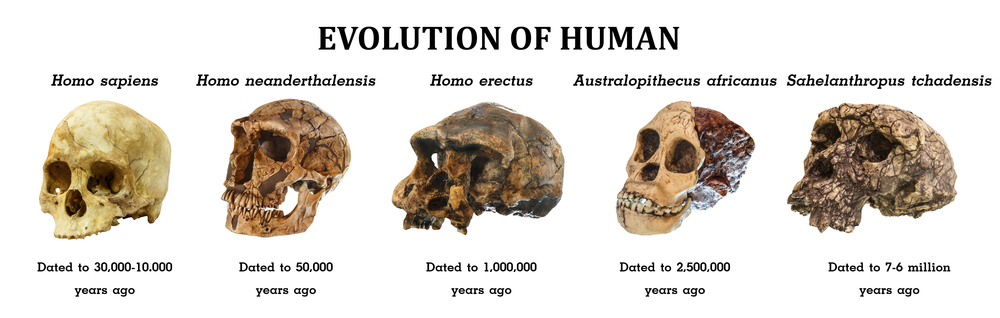
The analysis suggests that this species resembles us more closely than even Neanderthals.
Remember that human evolution is not as linear as everyone makes it out to be. There was a time when a number of different human species, such as Neanderthals, Denisovans, and modern humans, co-existed and inter-bred. But our species, Homo sapiens, for one reason or another, flourished and remains the only hominid alive today.
Another article giving a complete overview of human evolution can also be found on this website. Be sure to check that out if you’re curious to learn more about our evolution.
That being said, not all are ready to accept this skull as a new species. A professor from the University of Cambridge insists that Dragon Man is actually a Denisovan.
Denisovan (a different human species) was discovered after a group of Russian archeologists unearthed a human finger bone inside a Denisova cave in Russia. It is surprising that they found a pinky bone—and were even able to tell what it was!
Upon doing some DNA analysis, scientists at Harvard medical school and the Max Planck Institute found out that the DNA didn’t resemble Neanderthals or modern humans. Therefore, they called this new group of human species Denisovans.
Since Denisovans are said to have lived in Asia around 300,000 years ago, discovering a skull in China could mean that we might finally have a face for Denisovans.
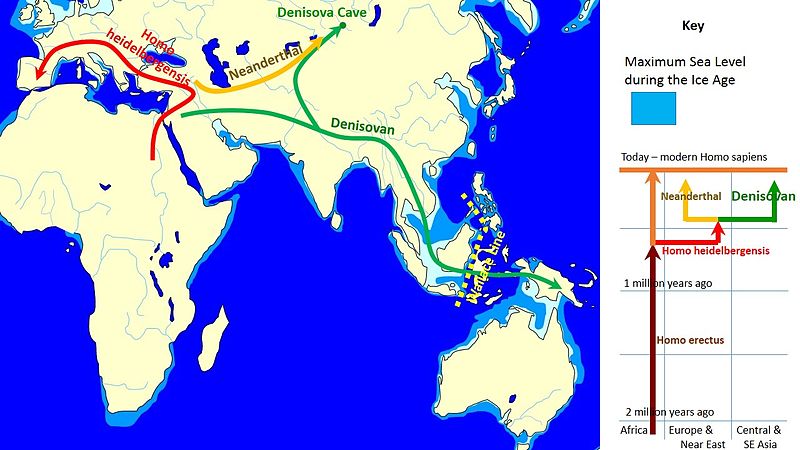
The author of the Dragon Man study agrees that it could possibly belong to the Denisovan species. He told Live Science, “[…] But until we have a complete Denisovan genome with a complete cranium (or better still, a complete skeleton!), we cannot resolve this question properly, only talk about probabilities.”
Conclusion
While stealing and hiding a skull for over 80 years is certainly frowned upon, the discovery of Dragon Man will hopefully give us new insight into the evolution of humankind. Only time will tell if Dragon Man rises to the rank of a new species, or if the skull will simply be immortalized for the strange backstory. Whatever the outcome, just remember that we all have the power to shape history, so long as we share our discoveries!
References (click to expand)
- Scientists hail stunning 'Dragon Man' discovery - BBC News. BBC Online
- The Story Behind China's 'Dragon Man' Discovery - Sixth Tone. Sixth Tone
- Ni, X., Ji, Q., Wu, W., Shao, Q., Ji, Y., Zhang, C., … Stringer, C. (2021, August). Massive cranium from Harbin in northeastern China establishes a new Middle Pleistocene human lineage. The Innovation. Elsevier BV.
- Ji, Q., Wu, W., Ji, Y., Li, Q., & Ni, X. (2021, August). Late Middle Pleistocene Harbin cranium represents a new Homo species. The Innovation. Elsevier BV.
- New human species 'Dragon man' may be our closest relative. Live Science
- Shao, Q., Ge, J., Ji, Q., Li, J., Wu, W., Ji, Y., … Ni, X. (2021, August). Geochemical provenancing and direct dating of the Harbin archaic human cranium. The Innovation. Elsevier BV.
- The Pleistocene Epoch - UCMP Berkeley. The University of California Museum of Paleontology
- Spelunking for Genes | Harvard Medicine magazine. Harvard Medical School
- Ancient Siberian cave hosted Neanderthals, Denisovans, and .... Science












