Table of Contents (click to expand)
A 360-degree camera parking system utilizes feeds from cameras embedded in the vehicle’s body to help the driver park efficiently.
Even the best drivers have experienced a minor scuff or fender bender at some point while maneuvering through tight spaces. Such damage can vary from something as inconsequential as a scratch to something that will demand an expensive visit to the mechanic.

In the good old days, people had to rely on rear view mirrors, instinct, judgement, or even human assistance to help with parking. However, the intelligent use of modern sensor and imaging technologies has enabled sophisticated parking assistants to be built in to automotive systems.
Recommended Video for you:
What Is 360-degree Camera Parking?
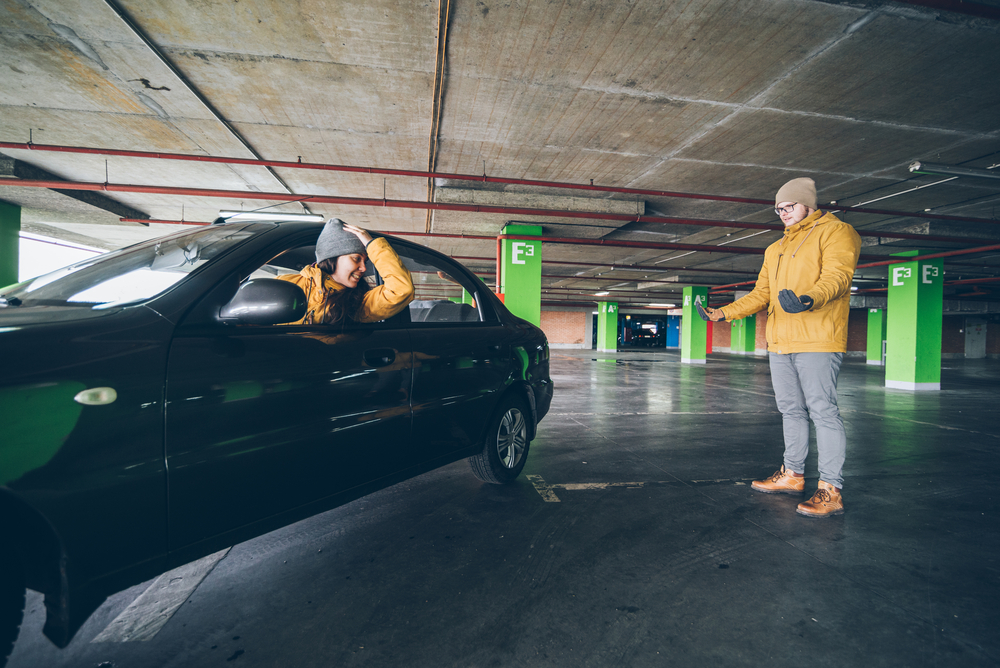
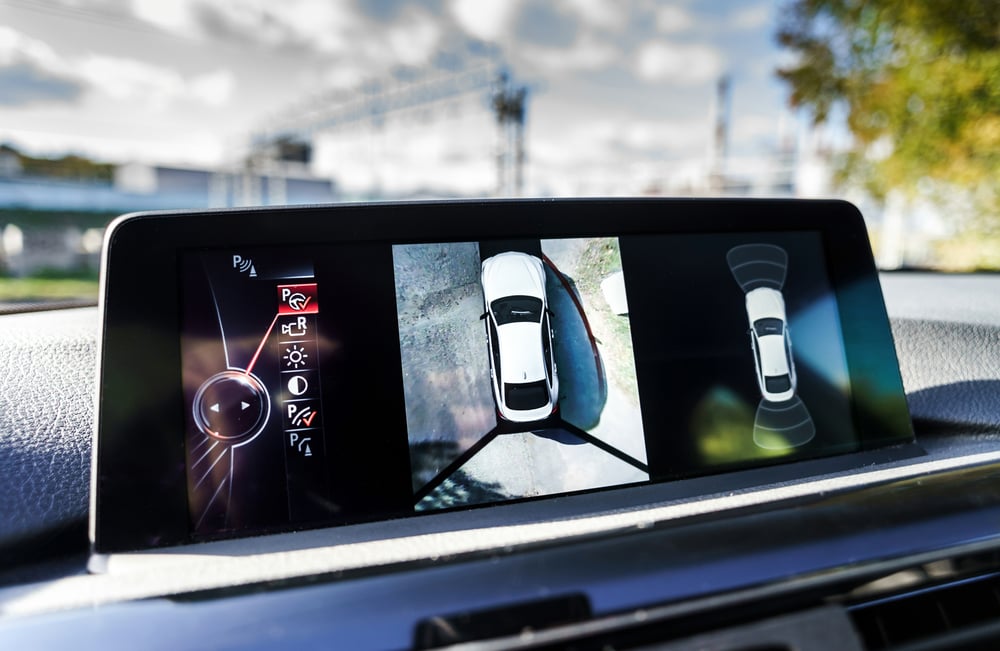
A 360-degree camera parking system consists of cameras and sensors that generate a virtual bird’s-eye view of the car, relative to its surroundings. The information is displayed on a screen inside the vehicle, enabling the driver to park efficiently.

Elements Of A 360-degree Camera Parking System
A 360-degree camera parking system is a combination of hardware and software that work in conjunction to display surrounding information to drivers in real-time.
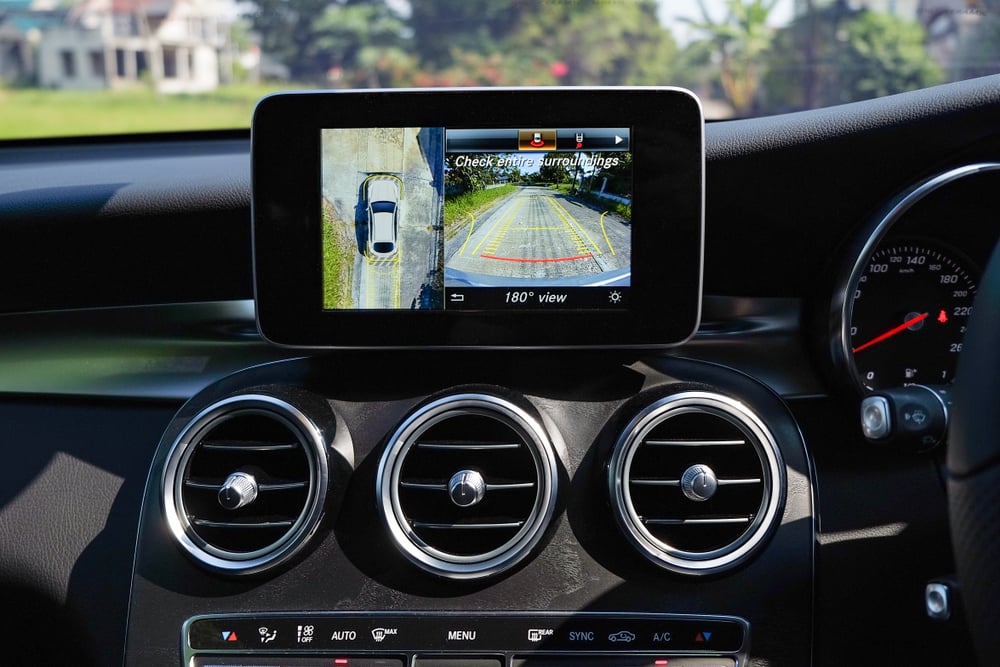
Cameras
The system is composed of 4 wide-angle lenses embedded in the body panels of the car, namely in the front grille, under the outside rear-view mirrors, and on the tail. The tail-mounted camera doubles as the reversing camera and can operate independently of the other three cameras.
These cameras are strategically located to ensure that the entire perimeter of the car is surveilled.
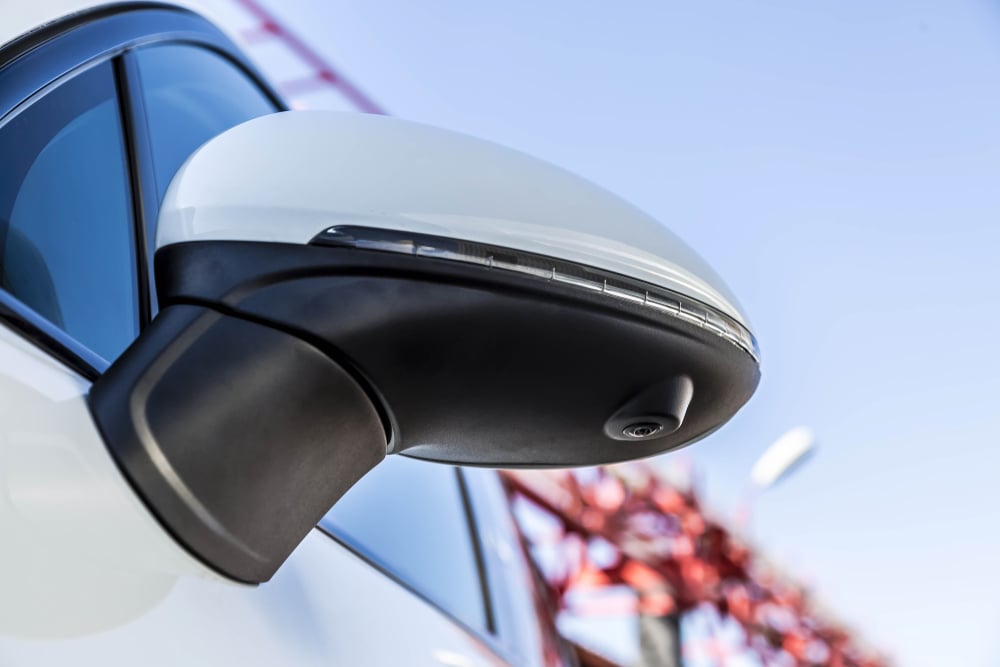

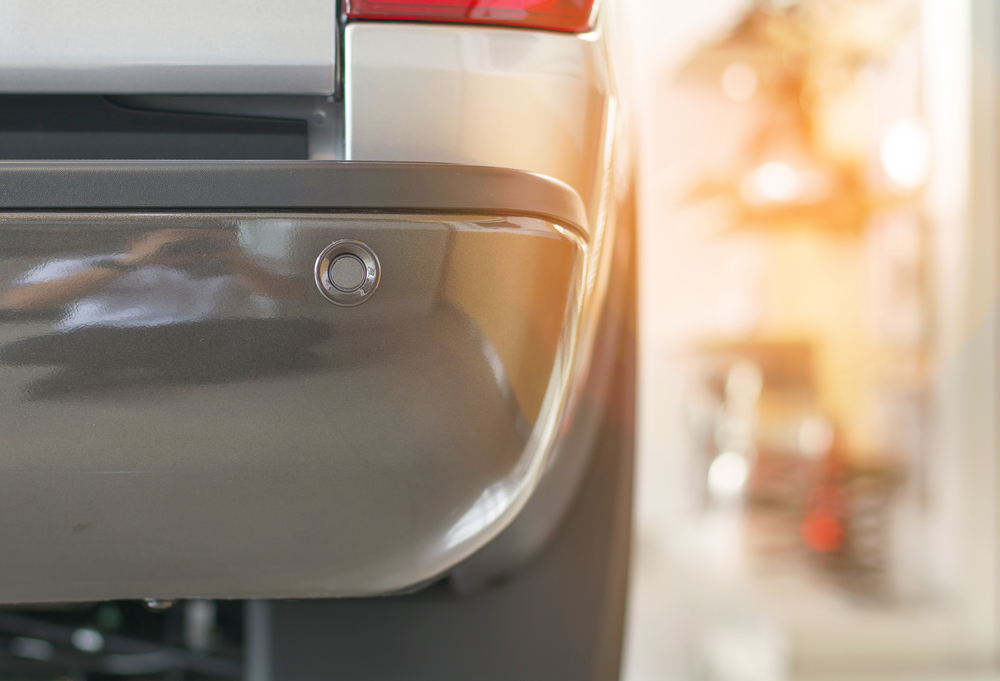
Proximity Sensors
A proximity sensor is an ultrasonic or electromagnetic device that sends corresponding signals and estimates the distance of the obstacle, based on the time it takes for the signal to be reflected. While proximity sensors are usually embedded in the front and rear bumpers, bigger cars often include them in the fenders for added safety.

Imaging Software
The cameras feed individual images to imaging software that is integrated into the parking system. This software stitches these images together to generate a virtual aerial view, taking into account all the obstacles around the car.
Representation Hardware
Parking assistants are usually audio-visual in nature. The video feed from the imaging software is directed to a screen in the car, which would either be the infotainment system or a dedicated module. It is further assisted by sonic or tactile feedback mechanisms that are used to alert the driver of proximity to an obstacle.
How Does A 360-degree Parking System Work?
A 360-degree parking system works in both forward and reverse gears, considering that a car may go back and forth multiple times before it is appropriately parked. It activates automatically upon selecting the reverse gear and can remain active in the forward gear for low speeds up to 10 km/h.
Imaging and visual representation is the most complicated part of this system. To make a coherent composite image for the driver, it’s essential for the imaging software to perform these functions:
1. Hemispherical aberration elimination: To eliminate image distortion resulting from the use of wide-angle lenses for accurate overlapping of images from the camera.
2. Exposure compensation: To match the lighting conditions on the images of all cameras.
3. Continuity of ground lines: To ensure the seamless transition from ground images of one camera to its adjacent counterpart so they don’t appear broken/discontinuous.
4. Image occlusion correction: To prevent overlapping/doubling of objects present above ground level.

After performing these corrections, the software uses a warping algorithm to juxtapose and blend these images into the final image, which is then projected onto the driver’s screen. As the car moves, the images also change in real-time, thereby giving the driver an accurate idea of his immediate surroundings. The display gets divided into two parts, one dedicated to the aerial view of the car, while the other projects the feed from the rear-facing camera.
In addition to the live video feed, the driver is also assisted by a buzzer, or a vibration function on the steering wheel, to alert him of any obstacle in the camera’s range.
Applications And Advancements
Considering that motor vehicle regulations are more safety-oriented than ever before, the importance of 360-degree parking systems has increased. From being a feature limited to luxury and high-end cars, they have now become essential equipment on all kinds of vehicles.

360-degree parking systems are an integral part of self-parking cars, wherein the car scans the road to find a suitable parking space, then takes control of the steering wheel to park itself. This is particularly helpful in tricky situations, such as parallel parking.